Usually, when you see lesions on your fingernails or toenails, your first instinct is to run to the drugstore for an anti-fungal ointment. However, the reasons for such changes can be completely different, in fact, non-fungal diseases of fingernails or toenails sometimes act only as symptoms of other destructive processes taking place in the body.
Causes of unhealthy nails
Normally, the nail should be smooth, not compacted, and pink. If it changes color, shape, becomes brittle and fragile, the nail plate partially or completely moves away from the phalanx of the finger, this may indicate the presence of the following problems:
- improper care of fingernails and toenails;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules;
- the presence of infectious or parasitic diseases in the body;
- injuries;
- the regular destructive effects of harmful substances;
- a congenital disorder that can only appear over time;
- organ system diseases - cardiovascular, nervous, endocrine;
- the formation of a low-grade tumor.
In addition, nails are subject to age-related changes. As they age, they can turn yellow and become hard or brittle.
Description of diseases
Simultaneous diseases of fingernails and toenails are quite rare, usually the nails of the upper limbs are affected.
Hippocrates nails
The outer phalanges of the fingers thicken, the nails become convex and rounded. Hippocrates was the first to describe this phenomenon affecting the hand, hence its name. It is not an independent disease, but it can appear as a symptom if:
- emphysema;
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- long-term endogenous poisoning;
- cardiovascular disorders;
- cancer, especially in the lungs.
Sometimes Hippocratic nails can be a hereditary or congenital pathology. In the case of cancer, it develops quickly in months or weeks, in other cases the change process can take years.
Scleronychia
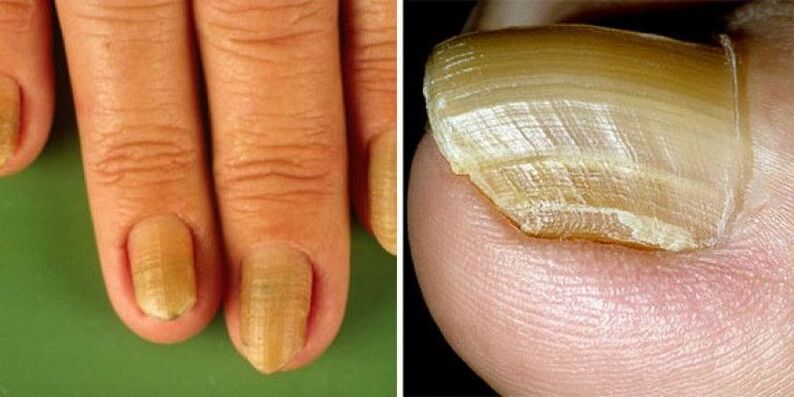
Hypertrophic changes occur in both arms and legs. The nails harden, become transparent, acquire a yellowish-gray hue, and may separate from the nail bed over time. It is a manifestation of endocrine diseases, although the main causes of scleronychia are still unknown.
Onychogryphosis
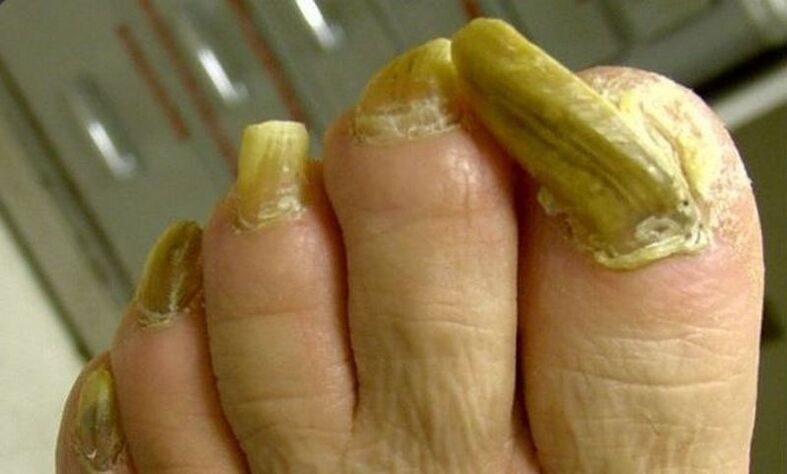
Another name is "bird's claw". It can develop as a result of frostbite or severe bruising.
The nail becomes thick and uneven, takes on an unnatural color from grayish yellow and brown to almost black. In addition, its free edge is bent like a bird's or twisted into a spiral.
The treatment consists of softening the surface of the nail with a salicylic plaster or ointment, in advanced cases it can be scraped off or surgically removed.
Onyhauxis
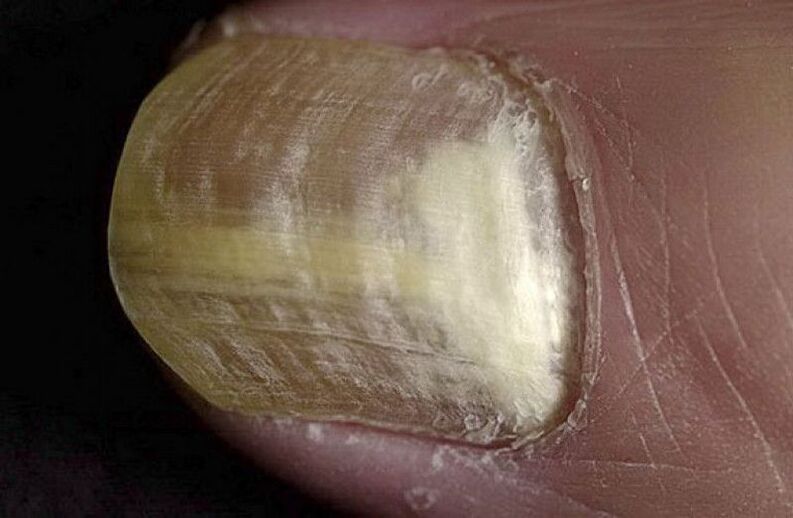
Overgrowth of the subungual cornea, which is accompanied by darkening of the nail and inflammation of the nail fold. It affects 1-2 fingers, in rare advanced cases it can be observed on all fingers and toes. It usually manifests itself as a consequence of insufficient nail nutrition in diseases such as:
- diabetes;
- varicose veins;
- atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities;
- elephant disease.
It can also be caused by an injury or a poor-quality manicure, sometimes onychauxis warns of a lack of certain vitamins and minerals in the body. For correction, blood circulation-thinning and stimulating drugs are prescribed, and in case of vitamin deficiency, the menu is enriched with essential nutrients and multivitamins.
Onychomadesis
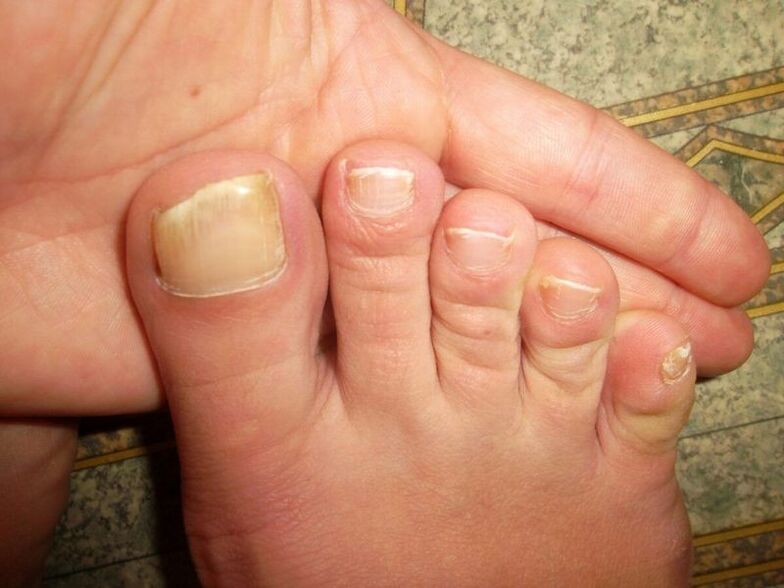
It sometimes accompanies fungal or bacterial disease of the fingernails and toenails, often as a result of mechanical injury or regular nail biting (onychophagia). The nail bed becomes inflamed, the nail matrix itself darkens and after a short time completely separates from the finger. Depending on the cause of the disease, this is done both from the free edge and from the inside.
The aim of the treatment is to improve blood circulation in the painful finger with the help of massage, vitamins and medicines. If onychomadesis is of infectious origin, the disease causing it is treated accordingly. In addition, they try to protect the exposed nail bed from fungi and bacteria, otherwise the affected nail will never grow back.
Beau's transverse furrows (Beau-Reil lines)
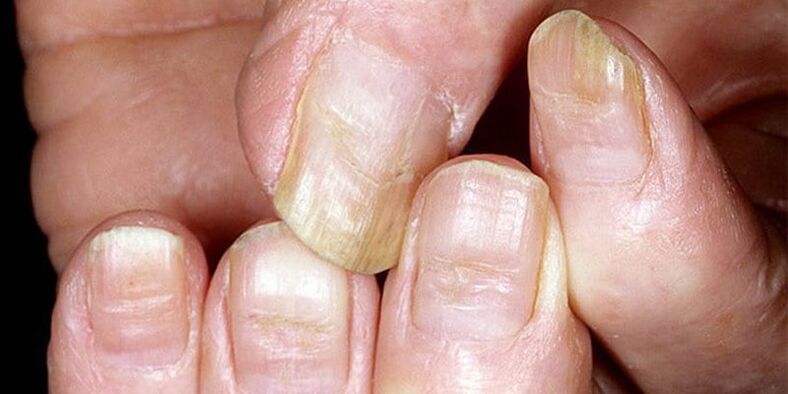
They appear due to the inhibition of the growth zone of the nail due to metabolic disorders, injuries or unsuccessful manicure, and often appear in children as a reaction to a viral infection. Depending on the course of the disease, there may be one or more that make the nail appear wavy (see image above).
Bo's line looks like an arc that extends across the entire surface of the nail from one side cylinder to the other. Its depth can reach 1 mm and directly depends on the severity of the disease. In severe cases, the groove can stretch the nail so much that the free edge does not receive enough nutrients, gradually withers and detaches from the finger.
After the elimination of the factor that caused the appearance of the Bo line, the defects of the nails disappear over time.
Longitudinal grooves
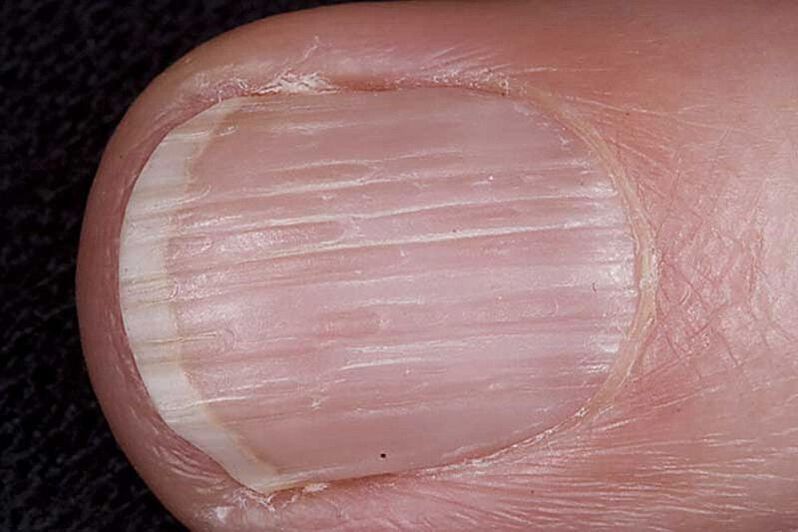
Also called vertical. Possible reasons for their appearance:
- age-related changes;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- psoriasis;
- spinal cord damage;
- gout;
- malfunctions of the intestines or pancreas;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- lichen planus;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- damage to the root of the nail plate;
- iron and vitamin B12 deficiency.
After eliminating the cause, the nails themselves will return to their original appearance. In order to improve the appearance during treatment or age-related changes, the longitudinal grooves can be hidden under a special varnish layer.
Leukonychia
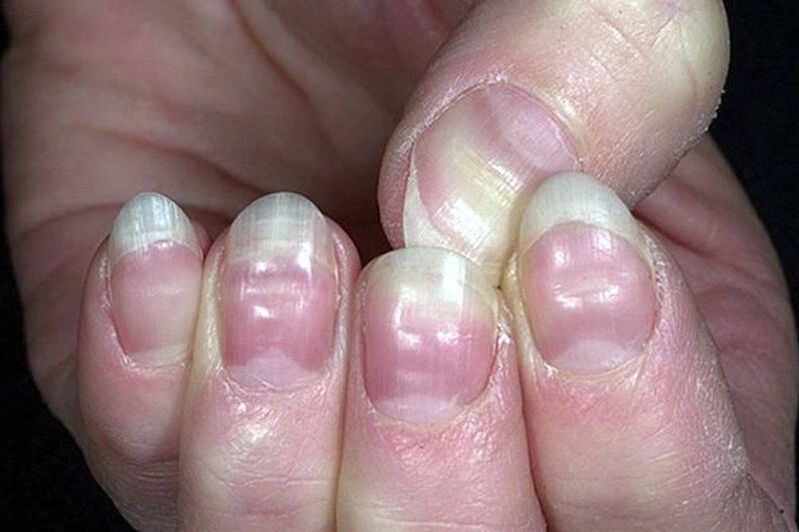
White spots appear on the nails. Their shape, quantity and location vary depending on the body's various dysfunctions. The appearance of spots on the nails indicates the presence of the following problems:
- protein deficiency;
- lack of vitamins (especially C, E, A) and trace elements (calcium, zinc, iron);
- mushroom;
- disorders of metabolic processes in the body;
- strong load on the nervous system: stress, depression, anxiety;
- intestinal problems;
- frequent contact with household chemicals, low-quality varnishes;
- cardiovascular disorders;
- kidney disease;
- skin diseases.
If there is no suspicion of illness, then this error can be corrected independently. It will be enough to establish a rest and work schedule, supplement the diet with foods containing essential nutrients, and wear gloves when in contact with household chemicals.
Onychodystrophy
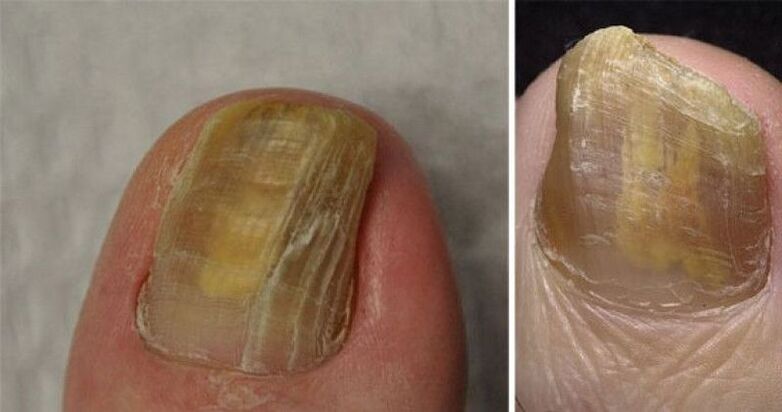
Changes occur in the periungual fold, nail plate and bed. The nail becomes less transparent, its thickness changes, and its growth slows down. It is also possible that longitudinal furrows may appear and the color changes to grayish yellow. The causes of this nail disease can be:
- mycoses;
- injuries;
- skin diseases (psoriasis, eczema, lichen planus);
- avitaminosis;
- chronic diseases of the endocrine system;
- heart and lung problems;
- interaction with alkalis, acids, chemicals with unprotected hands.
Onycholysis
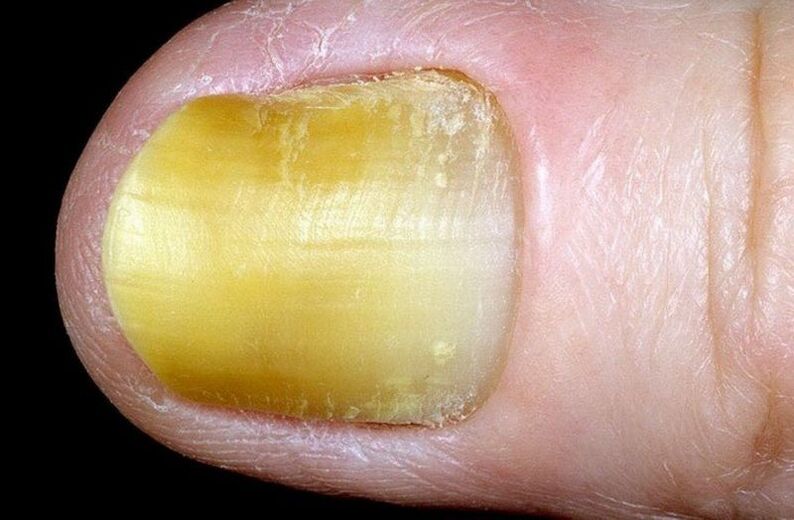
Refers to onychodystrophy. In case of onycholysis, the color of the nail plate changes from yellow to brown. The nail becomes brittle and partially or completely separates from its bed. Possible reasons:
- fungal and bacterial infections;
- skin diseases;
- taking antibiotics;
- dysbacteriosis;
- injuries;
- contact with allergens;
- some chronic diseases.
Ingrown toenail
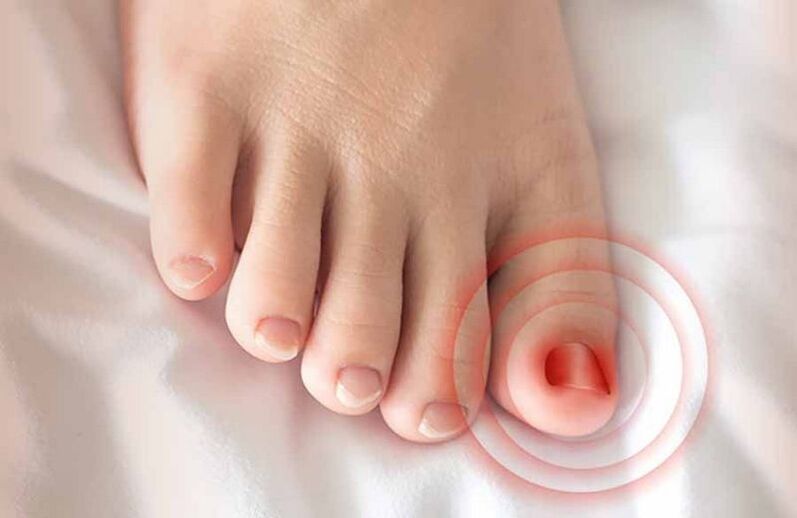
This type of nail disease occurs because the main causes are too tight shoes and improper trimming. The nail grows into the lateral pad, causing swelling of the finger, pain when walking, and inflammation of the soft tissues.
In milder cases, it can be treated with a foot bath or softening poultice, in more advanced cases, only a surgeon can correct the ingrown toenail.
Onychorrhexis
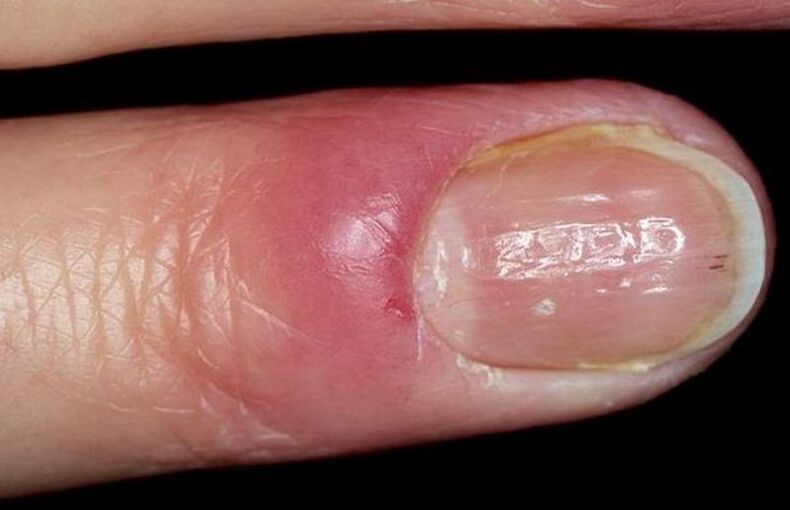
Brittleness and fragility of the nails, which leads to their separation. It usually accompanies diseases and conditions that damage the microcirculation in the fingers. A hard diet and frequent contact with an alkaline environment can also be the cause. Onychorrhexis is extremely rare on the legs.
Anonychia
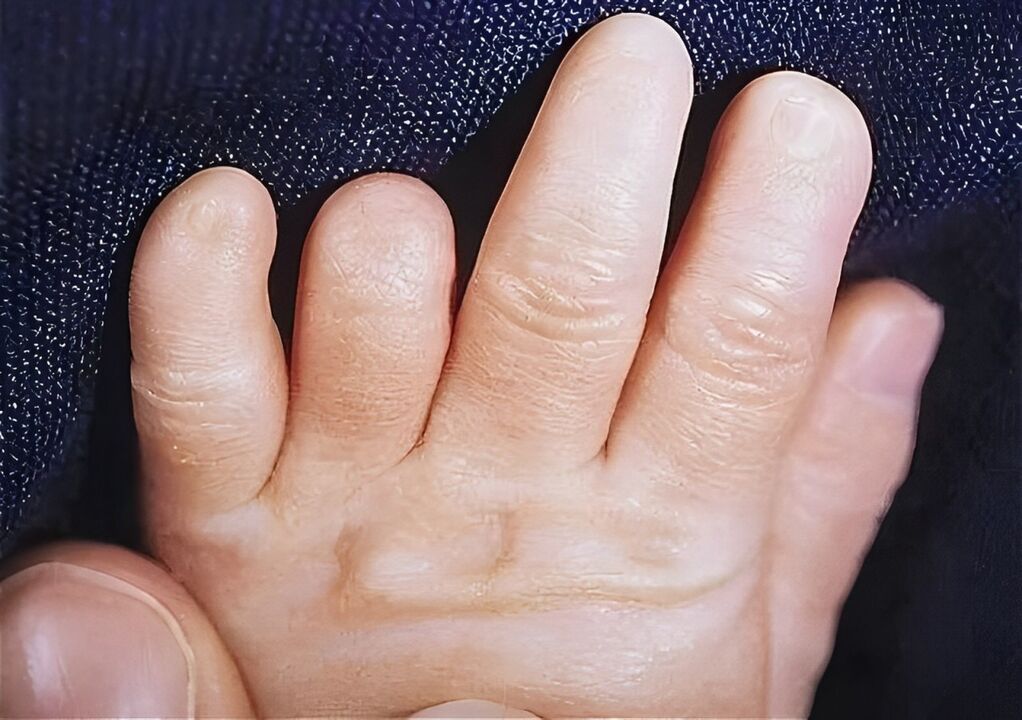
Absence of the nail plate. It can be a congenital or acquired injury, nervous system diseases of organic origin or certain dermatoses.
Koilonychia
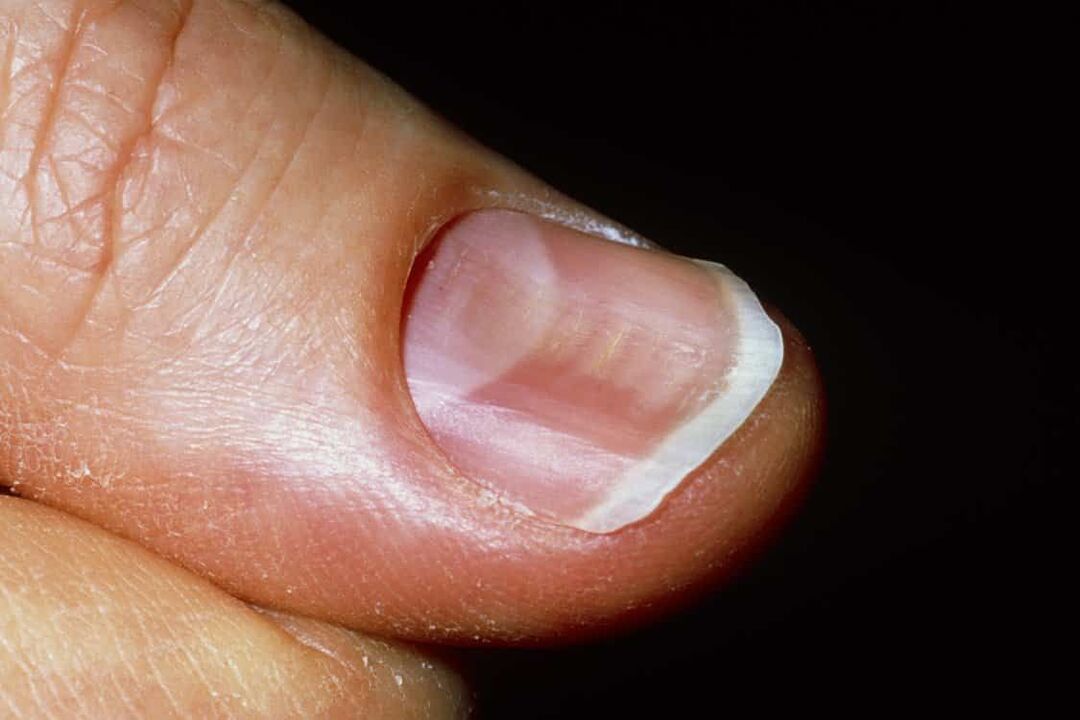
The nail becomes thin and concave like a spoon. Possible reasons:
- heredity;
- anemia;
- constant destructive effect of acetone or household chemicals;
- certain infections;
- improperly prepared manicure.
Micronychia
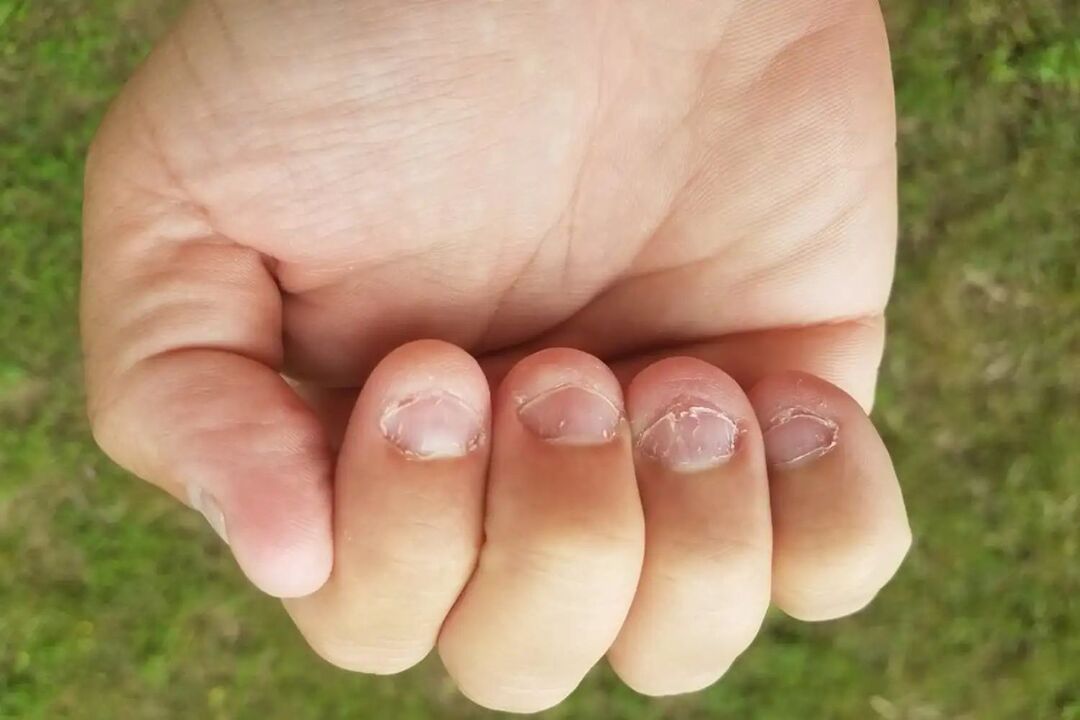
Abnormally small, shortened nails. It can be congenital or develop as a result of nail biting. Micronychia sometimes manifests itself as a symptom of diseases such as:
- progressive scleroderma;
- Trenaunay syndrome;
- flat angioma;
- True epilepsy;
- malnutrition of the hand.
Onychoschisis
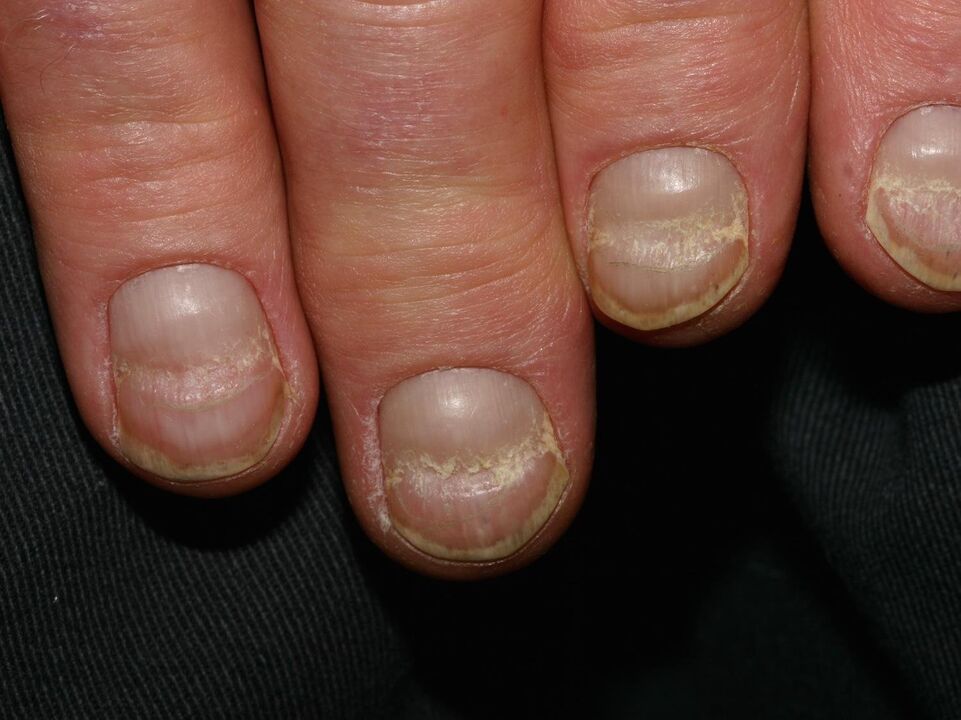
Transverse separation of the nail plate. It often occurs due to the aggressive effect of substances in household chemicals and decorative nail products. It often occurs in professions with increased mechanical stress on the fingers: musicians, printers. Onychoschisis also appears in case of vitamin deficiency.
Onychomycosis
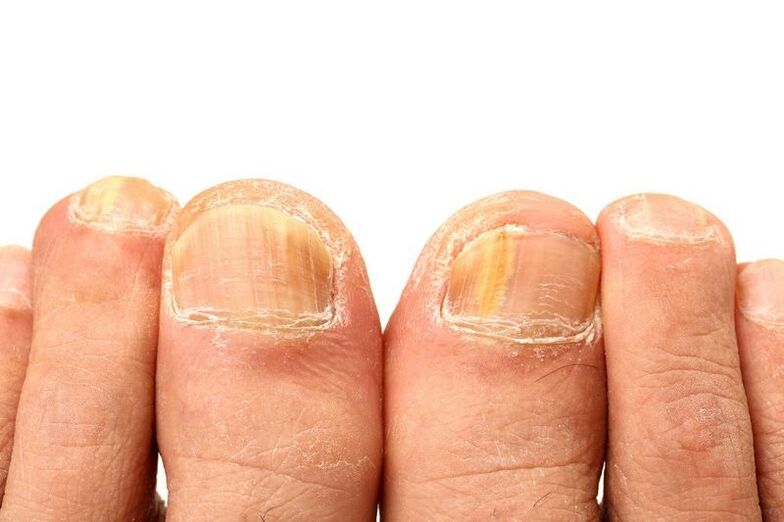
Fungal diseases of the nails are most often found on the feet, and there are quite a few types of them, so it is worth contacting a dermatologist for more effective treatment.
You can get the fungus anywhere, but it needs a warm, moist, dark environment for its development, so it mainly affects the feet. The development of the disease takes a long time, the first symptoms may appear only months later.
First, itching is felt in the infected area, the skin begins to dry and peel. Then the nail itself is affected, its color changes, cracks appear on the surface, and a putrid smell appears. If left untreated, over time, mycosis spreads throughout the body and causes various complications.
Gapalonychia
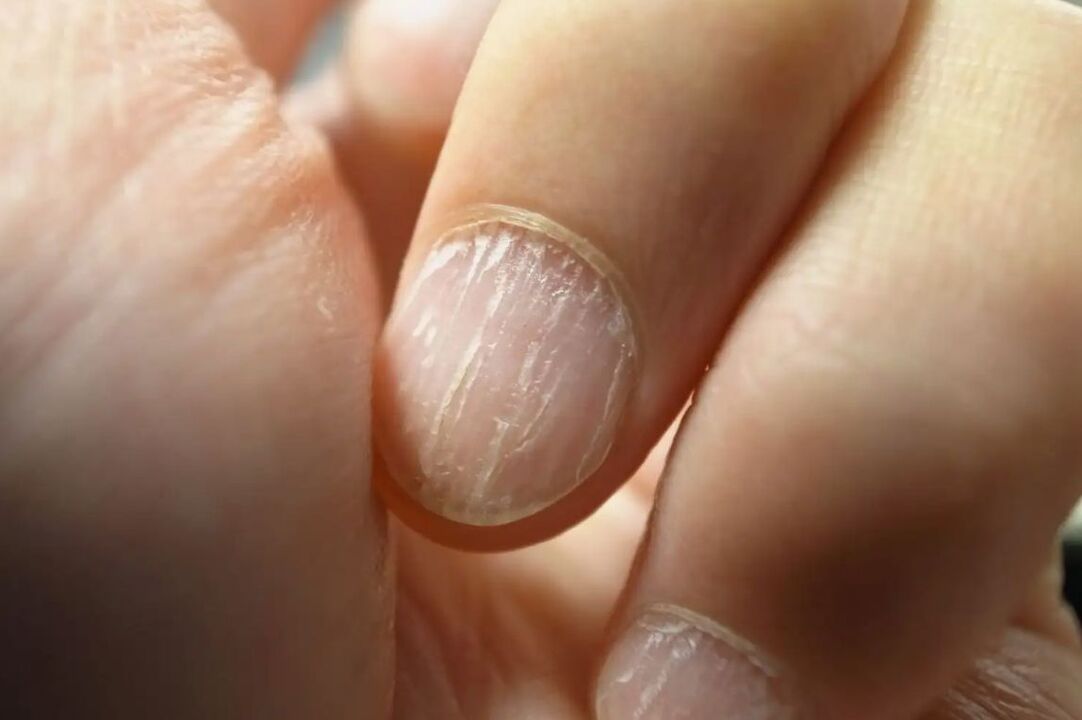
The nail plates become soft, chip and split. It occurs due to diseases of the endocrine system, metabolic disorders occurring in the body and regular exposure to aggressive chemicals.
Platonychia
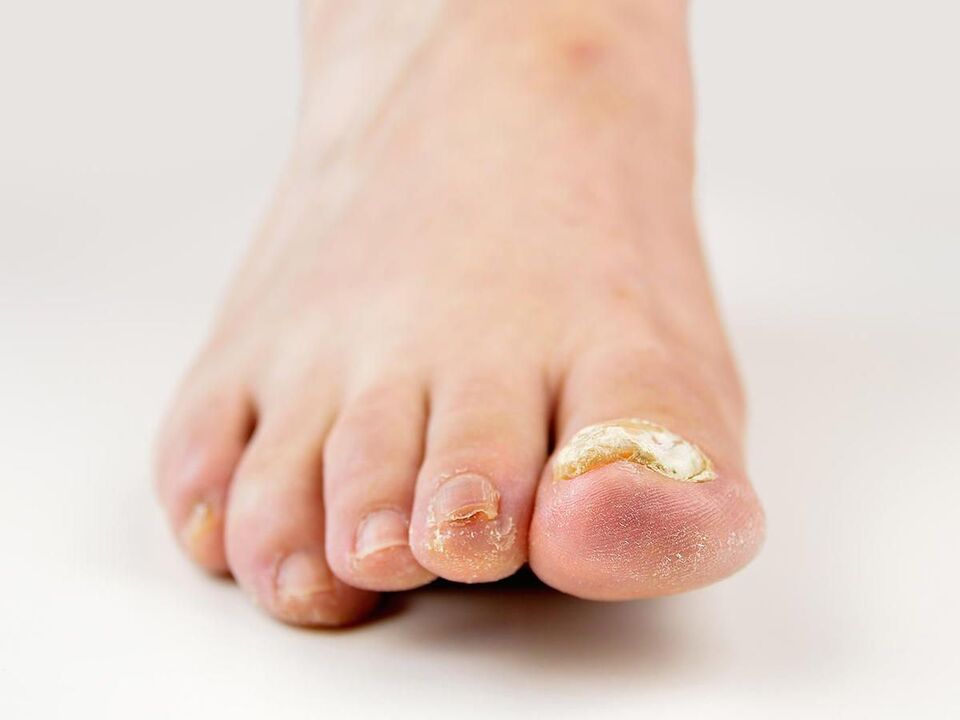
The surface of the nail is completely flat (see photo). It can be congenital or acquired as a result of professional activity. In addition, some chronic inflammatory processes can trigger this defect.
Prevention
The list of simple rules below will help prevent many possible diseases of toenails and nails.
- You can't bite your nails.
- File your nails with a glass or cardboard file.
- Manicure should be done with steamed hands, this reduces the risk of microtrauma and, as a result, wound infection.
- If you use the services of a salon to care for your nails, make sure that the technician disinfects the tools before use.
- Dry your hands and feet.
- The diet should include foods containing sufficient amounts of vitamins and minerals.
And most importantly, do not be lazy to contact doctors and do additional expert examinations. The earlier the disease is detected, the greater the chance of defeating it.